What Is Inflation?
Inflation can be defined as the reduction in purchasing power of a currency or the continued increase in prices of goods and services within an economy.
Inflation can be defined as the reduction in purchasing power of a currency or the continued increase in prices of goods and services within an economy. The increase in prices usually occurs in almost all goods in the economy, and it is not a sporadic event but rather sustained over a long period of time.
Causes of inflation
The causes of inflation go back to the basics of economics, that is, supply and demand. Essentially, there are two main ways that inflation can occur;
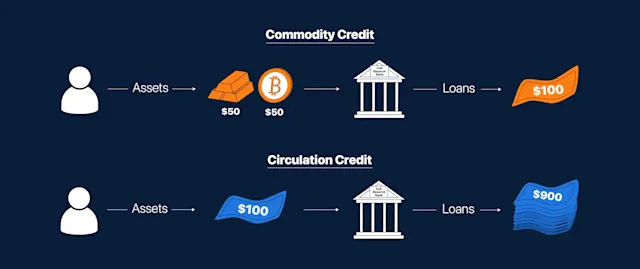
A rapid increase in the supply of a currency’s circulation would devalue the currency and cause inflation.
Secondly, inflation can be influenced by increased demand for goods; businesses can place higher prices because of the limited choices consumers have.
Robert .J. Gordon proposes the three-triangle model, which outlines the main events that could lead to inflation.
Demand-pull
This type of inflation occurs when there is an increased supply of money, either through government stimulus or lower interest rates. With more money in the consumer's pocket, positive consumer sentiment leads to higher spending and increased demand for goods that outweighs the supply. Producers are then able to increase the prices of the goods because they can still get customers due to the high demand. In 2020, the US government printed about 40% of the total dollar supply ever in existence, while interest rates were held down to 0% since 2018; this increased money supply is visible through the increasing inflation seen towards the end of 2021 and into 2022.
Cost-push inflation
An increase in prices for raw materials will lead to an increased production cost that forces businesses to adjust for profits by “pushing” the extra costs onto the consumer. This can be caused by supply chain shortages or government policies (e.g., increased wages, increased taxes & tariffs, import sanctions). A great example is the Covid-19 pandemic which forced governments to impose restrictions on travel and transportation; this limited supply chains, which lead to a lower supply of goods and services while demand remained the same if not increased.
Built in- inflation
This type of inflation relates to adaptive expectations; it is the idea that people expect inflation rates to continue. Essentially, people look to the past and see that inflation existed; thus, they believe that it will persist in the future; for example, employees negotiate higher wages to keep up with the incoming inflation. This causes businesses to have higher production costs, thus forcing them to increase the prices of goods, which then cycles back to inflation and employees requesting higher wages. As seen in this scenario, the wage spiral continues, and one factor continues to trigger the other.
How to measure inflation (CPI)
Most nations measure inflation over annual periods, but it can also be tracked for months. There are various indices that can be used to calculate inflation, such as the Wholesale Price Index (WPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), and the most commonly used Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Understanding CPI
The CPI is a basket of various consumer goods that examines the weighted average prices of goods and services used by consumers. It is calculated by taking the price of each consumer good and averaging it based on its relative weight to the other products in the basket. The prices used are those that a retail consumer would purchase them for. The agencies tasked with this statistic use various sources for their data to ensure their final findings are accurate as possible.
The change in CPI is associated with the changes in the cost of living, which can be used to identify inflationary and deflationary times.
How to slow down inflation
When inflation is not corrected, it can be damaging to the economy, and this can be corrected by governments through monetary or fiscal policy.
Quantitative Tightening (QT): The central bank of a country is usually tasked with managing the economy and are given the power to control the currency supply. Central banks can introduce QT, a measure that reduces the money supply to try and curb inflation; although this method is not always effective, thus other measures must be taken.
Higher interest rates: High-interest rates make it more expensive to borrow money which discourages consumers and businesses from borrowing more money and spending. Although, such measures do hinder the growth of the market and could result in market crashes.
Fiscal policy: This refers to the government’s control over spending and taxes. By increasing taxes and decreasing government spending (subsidies, social programs, etc.), consumers and businesses are left with less disposable income to spend, which can curb inflation. Although, this can be seen as controversial and spark public outrage.
How can Bitcoin & Cryptocurrencies help
Given that inflation is always a constant threat, people rely on investing in assets that will protect their value over time. Historically, many invest in the traditional market through stocks, bonds, commodities, and real estate, and more commonly rely on gold as an inflation hedge. Since the introduction of cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin has been relied upon as the new digital gold among other investments within the cryptocurrency space. Below are a few ways that blockchain technology can offer a way of hedging against inflation.
Bitcoin: Inherently built to beat inflation. The supply will never surpass 21 million coins. This is a built-in feature that cannot be manipulated by any person or entity, including the creator. It is easy to transport and exchange even across borders. Its authenticity can be verified by anyone on the blockchain because it is an open-source system.
Stablecoins & DeFi: Decentralized finance has produced a new way for financial management outside the control of centralized entities. This has enabled developers to create investment applications with higher returns than traditional investments. Given that cryptocurrencies experience high volatility, which is scary to some investors, stablecoins provide a cryptocurrency alternative to hedging against inflation. Certain exchanges will offer staking or liquidity pools that enable customers to earn higher interest rates (up to 20%) on their savings, something not offered in traditional markets.
Readers should be aware that none of the information above is financial advice and that it is purely for educational purposes. The cryptocurrency space is still relatively new thus it comes with high volatility, and many products are still in the testing phase which carries a lot of risks. Kindly, DYOR and be aware that investment decisions should be independently at the end of the day.